Problem:
Bài toán thực tế:
Một căn nhà rộng , có phòng ngủ và cách trung tâm thành phố có giá là bao nhiêu. Giả sử chúng ta đã có số liệu thống kê từ 1000 căn nhà trong thành phố đó, liệu rằng khi có một căn nhà mới với các thông số về diện tích, số phòng ngủ và khoảng cách tới trung tâm, chúng ta có thể dự đoán được giá của căn nhà đó không?
Diễn dãi theo code:
h = so hang
c = so cot
Input:
h, c
x[1][1] ... x[h][c]
y[1] ... y[h]
x[h+1][1] ... x[h+1][c]
Ouput:
y[h+1]
Solve:
Ta co
θ[1] * x[1][1] + ... + θ[c] * x[1][c] ~ y[1]
...
...
θ[1] * x[h][1] + ... + θ[c] * x[h][c] ~ y[h]
=> θ[1]* x[h+1][1] + ... + θ[c]*x[h+1][c] ~ y[h+1]
=> Can tim cac θ de giai quyet bai toan
Ví dụ đơn giản:
Input: Cho tập điểm (x, y)
B1: Dự đoán θ0, θ1 (~ a, b)
B2: Cập nhập θ cho đến khi đạt điều kiện dừng (thường abs(dHMM) < epsilon, loop = ...)
θ_new = θ_old - alpha * dHMM
Cách tìm θi của bài toán trên
Code Python:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
np.random.seed(2)
def grad(w):
N = Xbar.shape[0]
return 1/N * Xbar.T.dot(Xbar.dot(w) - y)
def l(w):
N = Xbar.shape[0]
return .5/N*np.linalg.norm(Xbar.dot(w)-y, 2)**2
def myGradientDescent(w_init, grad, alpha, loop = 1000, esilon = 1e-4):
w = [w_init]
for i in range(loop):
w_new = w[-1] - alpha*grad(w[-1])
if np.linalg.norm(grad(w_new))/len(w_new) < esilon:
break
w.append(w_new)
return (w, i)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# dataset
X = np.random.rand(1000, 1)
y = 4 + 3 * X + .2 * np.random.randn(1000, 1) # noise added
# Building Xbar
one = np.ones((X.shape[0], 1))
Xbar = np.concatenate((one, X), axis=1)
# Gradient descent
w_init = np.array([[2], [1]])
(w1, it1) = myGradientDescent(w_init, grad, 1)
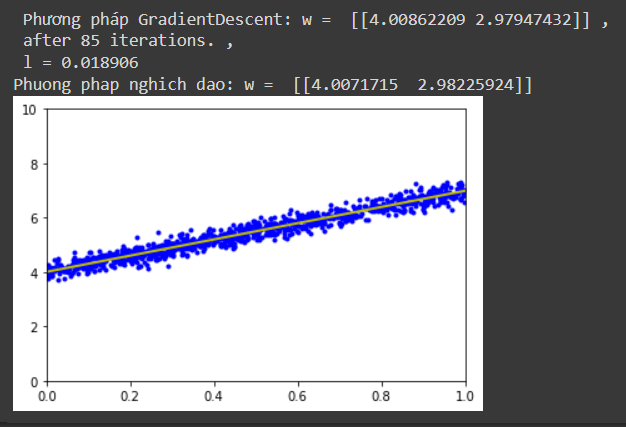
print(' Phương pháp GradientDescent: w = ', w1[-1].T, ',\n after %d iterations.' %(it1+1),',\n l = %f ' % l(w1[-1]))
# Linear regression
A = np.dot(Xbar.T, Xbar)
b = np.dot(Xbar.T, y)
w_lr = np.dot(np.linalg.pinv(A), b)
print('Phuong phap nghich dao: w = ', w_lr.T)
# Display result
w = w_lr
w_0 = w[0][0]
w_1 = w[1][0]
x0 = np.linspace(0, 1, 2, endpoint=True)
y0 = w_0 + w_1 * x0
# Draw the fitting line
plt.plot(X.T, y.T, 'b.') # data
plt.plot(x0, y0, 'y', linewidth=2) # the fitting line
plt.axis([0, 1, 0, 10])
plt.show()
Ouput:
Xem thêm bài viết cùng chủ đề: Gradient Descent cho hàm 1 biến




No comments:
Post a Comment